Which Is Better NiMH Battery vs Lithium-ion?
Intro: Why Comparing Battery Types Matters
Choosing the right rechargeable battery is critical for product performance, reliability, and cost-efficiency. Two of the most commonly used chemistries—Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) and Lithium-ion (Li-ion)—serve different needs across industries. Whether you’re powering a consumer device, medical instrument, or industrial tool, understanding the differences helps ensure you make the right choice.
What Batteries Actually Last the Longest?
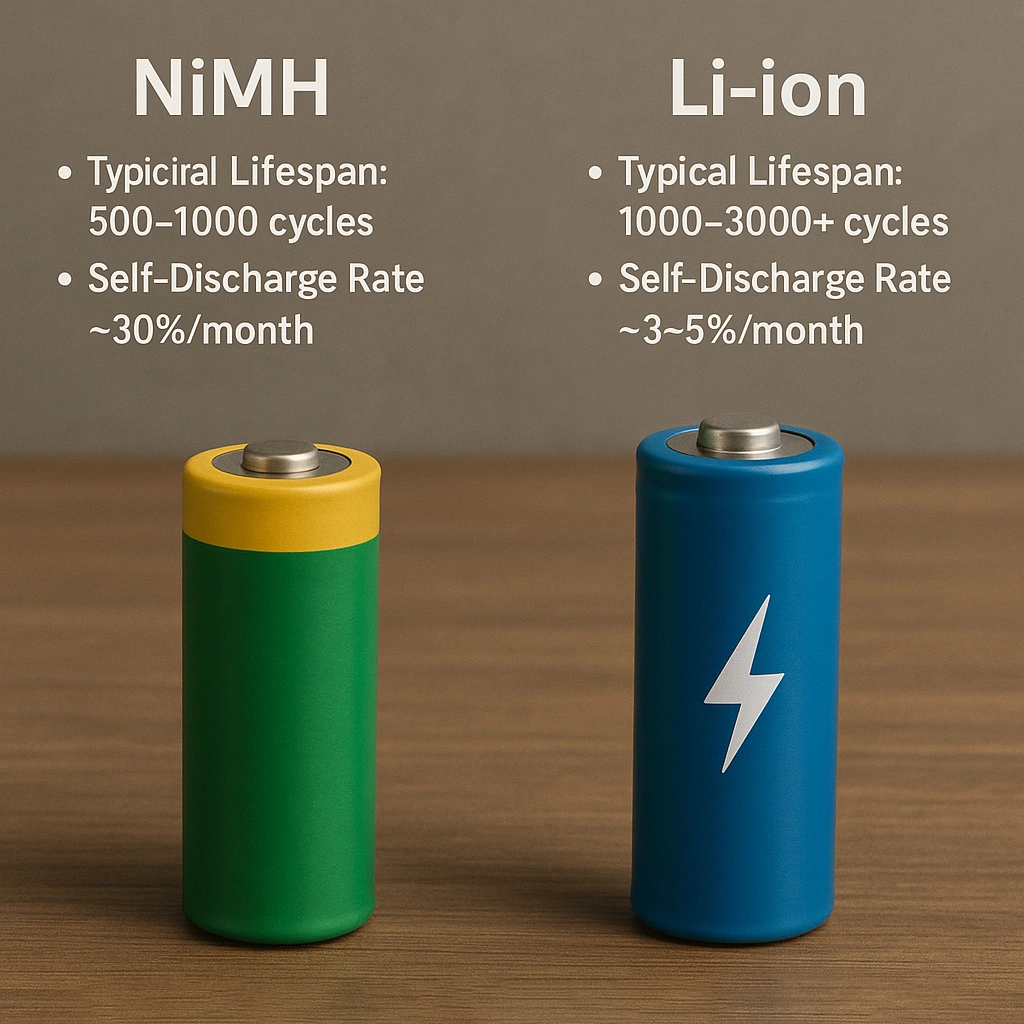
In terms of overall lifespan and energy retention, lithium-ion batteries significantly outperform NiMH batteries.
| Battery Type | Typical Lifespan (cycles) | Self-Discharge Rate | Memory Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| NiMH | 500–1000 | ~30%/month | Yes |
| Li-ion | 1000–3000+ | ~3–5%/month | No |
Which Has Longer Life NiMH or Lithium-ion Rechargeable Batteries?
Lithium-ion rechargeable batteries offer a longer usable life, both in cycle count and calendar years. NiMH batteries tend to degrade faster due to:
-
Higher self-discharge rates
-
Susceptibility to overcharging or deep discharging
-
Memory effect (capacity fade if not fully discharged)
Li-ion batteries, when properly managed, can deliver up to 10 years of service in some applications.
What Are the Advantages of a Lithium-ion Battery?
-
High energy density: More power in a smaller, lighter package
-
Low self-discharge: Maintains charge longer during storage
-
No memory effect: Doesn’t require full discharge before charging
-
Wide operating temperature range
-
Fast charging and high efficiency
These characteristics make lithium-ion batteries ideal for:
-
Smartphones and laptops
-
Medical and industrial equipment
-
Electric vehicles and energy storage systems
What Are the Disadvantages of NiMH Batteries?
While NiMH batteries are safer and more affordable in some applications, they have notable drawbacks:
-
Lower energy density: Require more space and weight for the same output
-
High self-discharge: Loses charge quickly when not in use
-
Memory effect: Reduces capacity over time if not properly cycled
-
Slower charging times
-
Shorter cycle life
These factors limit their use in modern high-performance or space-constrained applications.
Why Are Lithium-ion Batteries Better Than NiMH?
Lithium-ion batteries outperform NiMH in nearly every key performance category:
| Criteria | NiMH | Lithium-ion |
|---|---|---|
| Energy density | Lower | Higher |
| Self-discharge | High (~30%/month) | Low (~5%/month) |
| Weight & size | Bulkier | Lightweight & compact |
| Charge retention | Poor | Excellent |
| Memory effect | Present | Absent |
| Charging speed | Slower | Faster |
| Cycle life | 500–1000 cycles | 1000–3000+ cycles |
Unless your application requires extremely low voltage or low-cost options, lithium-ion is the superior choice.
Can You Replace NiMH Batteries with Lithium?
Yes, but with caution. You must consider:
-
Voltage differences: NiMH cells = 1.2V, Li-ion = 3.6V/3.7V
-
BMS requirement: Li-ion batteries require protection circuits
-
Size/form factor: May differ depending on casing
-
Charging method: Chargers for NiMH are not compatible with Li-ion batteries
For device upgrades or redesigns, manufacturers often switch to custom lithium-ion battery packs to improve performance, reduce weight, and extend runtime.
Conclusion: Lithium-ion Outperforms NiMH in Most Applications
While NiMH batteries still serve well in some low-power or legacy devices, lithium-ion batteries offer clear advantages in longevity, energy density, efficiency, and charging speed.
For modern electronics, portable equipment, or industrial solutions, lithium-ion is the preferred choice, especially when paired with a well-designed BMS.
If you’re considering switching from NiMH to lithium, consult with a battery solution provider like PKNERGY to ensure safe and optimized integration.